APINDO UMKM Collaboration with UK-ASEAN Mission:“Empowering Women Entrepreneurs and MSMEs through Regulatory Reforms.”
Thursday, 20 March 2025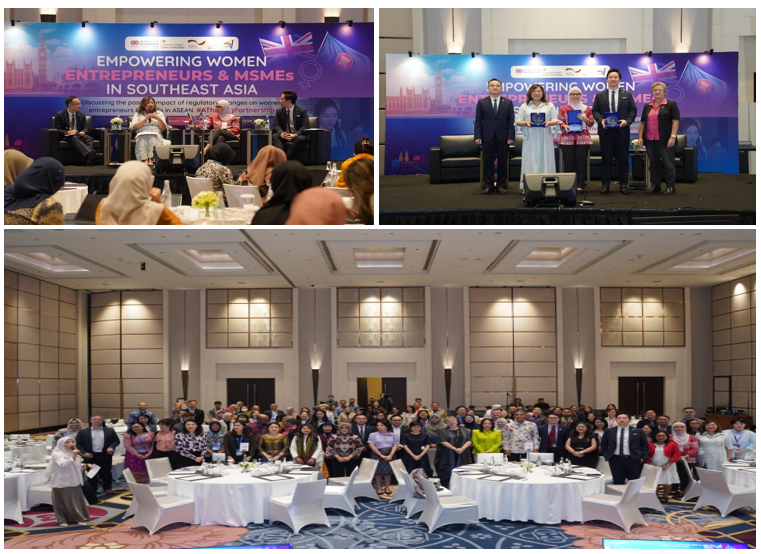
UK has conducted in ASEAN Member States a research is entitled “Empowering Women Entrepreneurs and MSMEs through Regulatory Reforms.” and launched the findings last 6 March 2025
This research was commissioned to support the evaluation and development of regulatory reforms in ASEAN, so that they can have the most positive impact on Women Entrepreneurs and Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in ASEAN Member States. It provides concrete recommendations that we plan to pursue in partnership with ASEAN as we implement the EIP.
The research was conducted by the Centre for Strategy and Evaluation Services (CSES) UK in several ASEAN countries including Indonesia, Malaysia, and Vietnam, to provide insights that we will apply as we develop the activities under our programme, in partnership with ASEAN sectoral bodies.
The event opened with a presentation of the findings and recommendations from the UK-funded research, followed by panel sessions on intellectual property, good regulatory practices, consumer product safety, and standards and quality.
Ibu Lishia Erza, as Committee Chair of SME Capacity Building & Inclusive Economy APINDO discussed with stakeholders involved in the empowerment of women entrepreneurs and MSMEs through regulatory reforms and APINDO’s advocacy work, particularly in building both SME and institutional capacity to enable women led and owned SMEs to leverage the value of intellectual property rights.
Women entrepreneurs play a crucial role in the ASEAN economy. In the last few years, there has been significant progress in recognising the role of women in the regional economy. There are no recent figures for the number of women owning a business across the region, but 2017 estimates have suggested a total of 61.3 million women owning and operating businesses in the ten ASEAN member countries, accounting for 9.8% of the total ASEAN population.
The findings show that:
• All of the countries under investigation are increasingly recognising the importance of women in their national economies and have developed strategies for increased inclusion and participation, including the creation of specific government departments and gender
budgeting, with these being increasing areas of focus.
• While predominantly, women-owned businesses are to be found in low-value sectors, there are some women who spearhead enterprises found in high-tech industries which provide important value to economies.